Step 1 - Setup a Basic Gateway
In this tutorial we'll setup a simple gateway. We'll use a demo API at todos.zuplo.io that acts as a todolist API.
This demo API is protected by an API key (sometimes called a shared secret) that
must be provided in an api-key header. Good news - given this is a demo API -
the key is provided in the unauthenticated error message.
To get started, sign in to portal.zuplo.com and create a free account. Create a new empty project. Then...
1/ Add a route#
Inside your new project, choose the routes.oas.json file and click Add
Route.
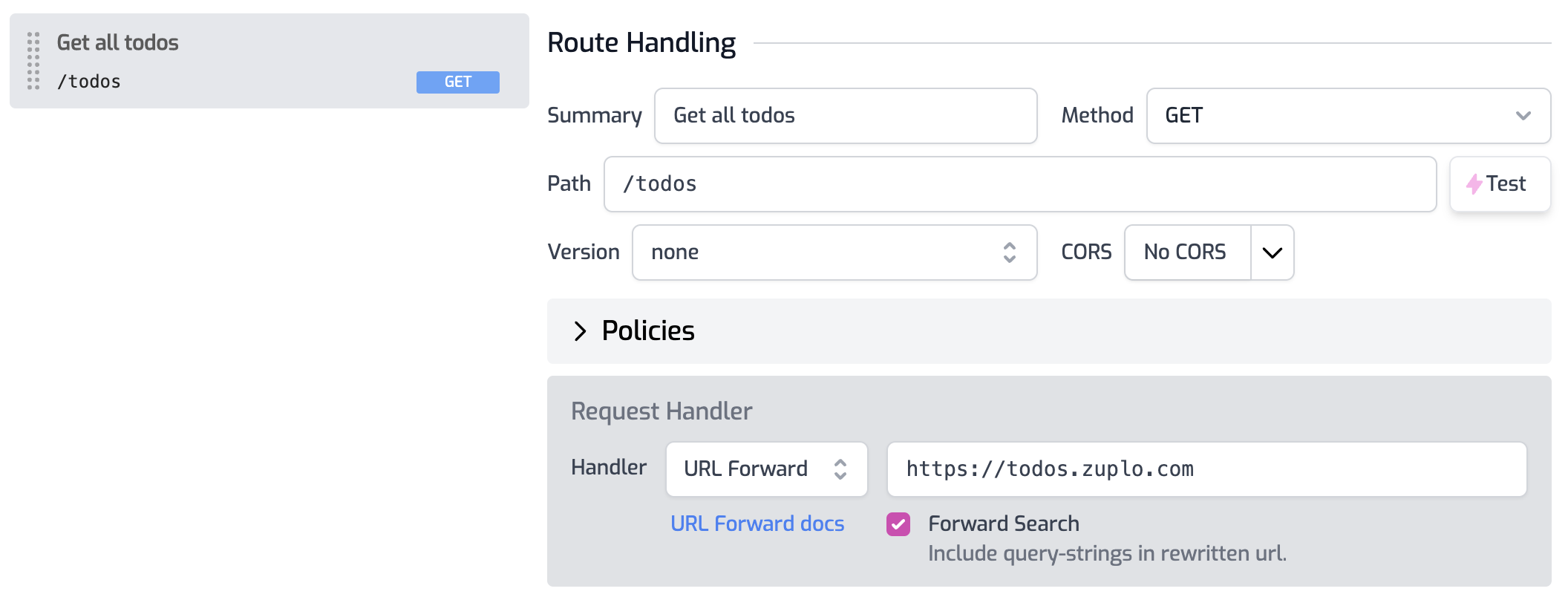
Using the Route Designer, let's configure our first route to handle the
GET /todos route.
- Summary:
Get all todos - Method:
GET - Path:
/todos - URL Forward:
https://todos.zuplo.io
Save your changes (you can click the disk icon next to routes.oas.json or
press CMD+S).
You can quickly test this route by clicking the Test button next to the Path field and clicking the URL in the dialog that opens.
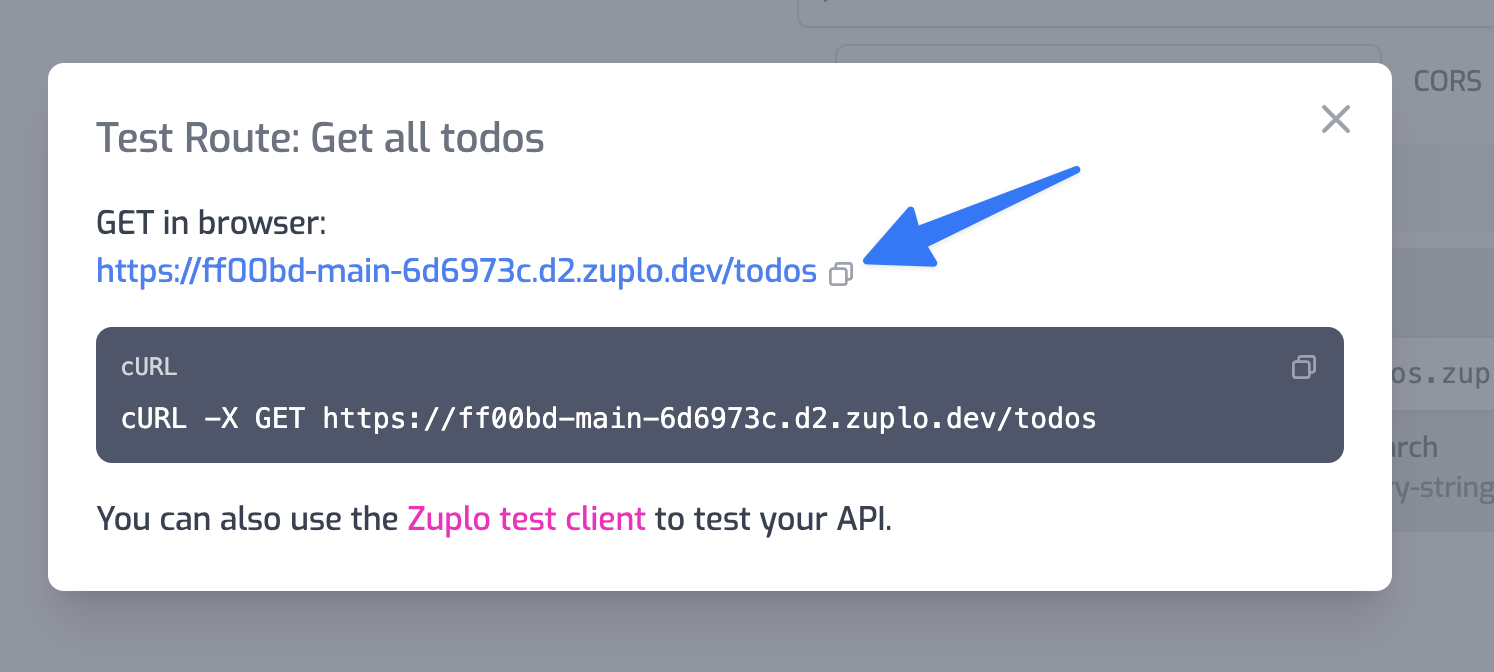
You should receive a 401 Unauthorized that says something similar to
{
"status": 401,
"title": "Unauthorized",
"detail": "No key or invalid key provided",
"type": "https://httpproblems.com/http-status/401",
"instance": "/todos",
"hint": "This is a demo API that requires authentication. You must add a header 'api-key' with a value '4f0aeaf7-d17f-4b2b-9b71-5177bd194759'"
}This is expected because you have not provided the required api-key header.
Copy the required api-key value from that error message to your clipboard
(e.g. 4f0aeaf7-d17f-4b2b-9b71-5177bd194759).
2/ Set the secret header#
Open the policies section in your route and click Add Policy to the request pipeline.
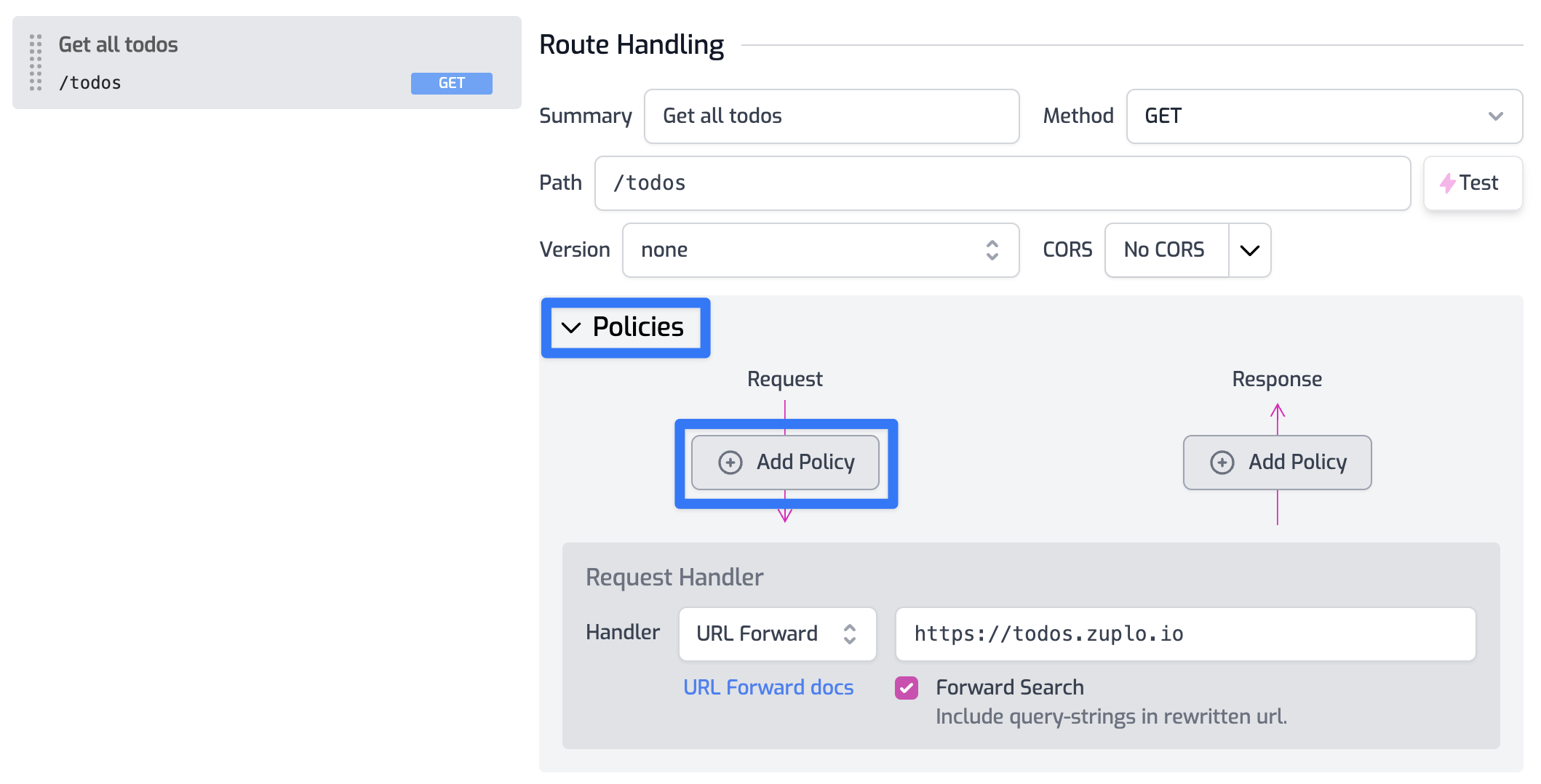
Find the Add or Set Request Header
Configure the policy JSON to set header name to api-key and the value to
$env(API_KEY). This tells the policy to read the value from our secure vault
used for Environment Variables.
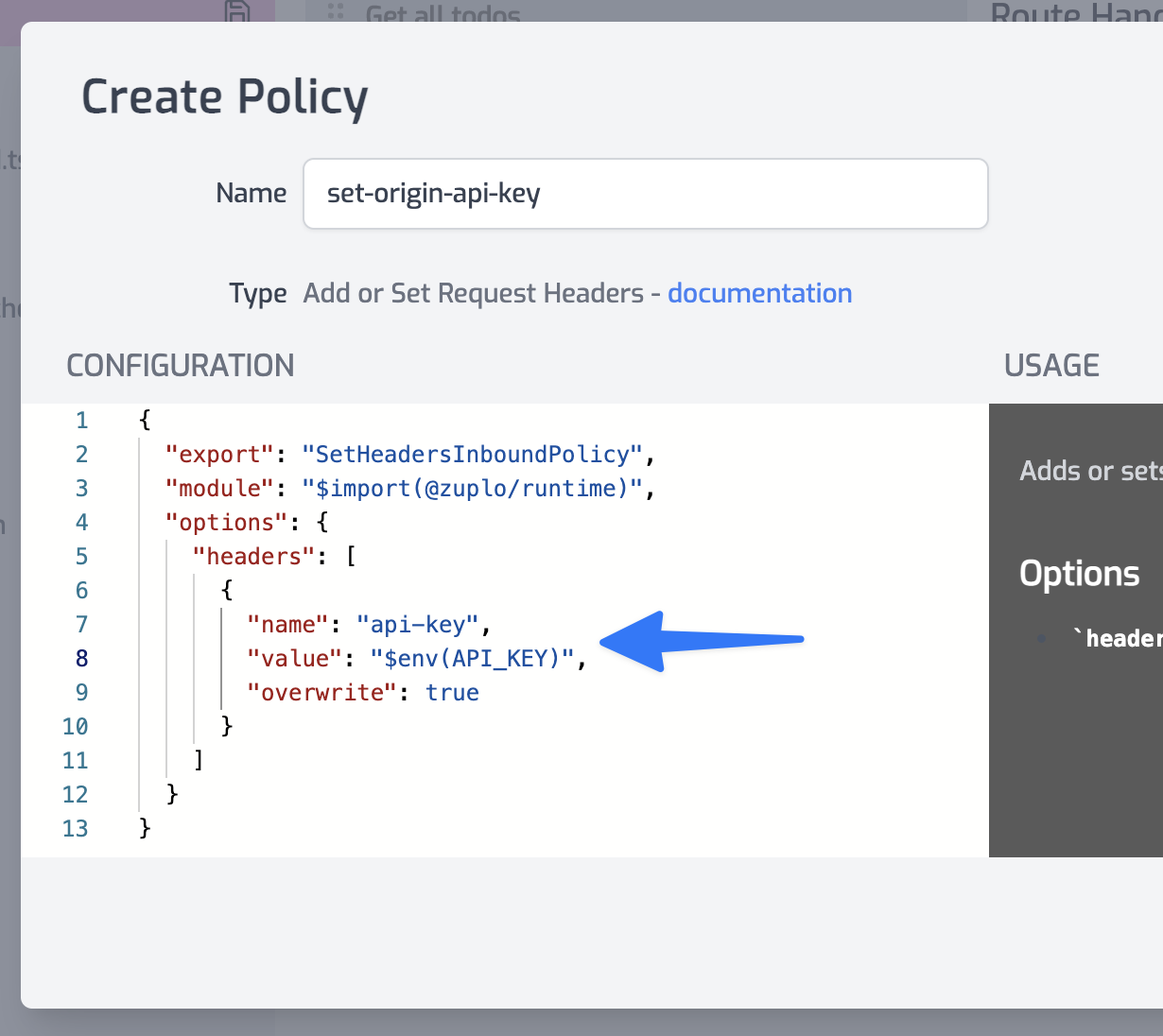
Save your changes to routes.oas.json.
Head over to the Environment Variables screen in settings and click Add new variable.
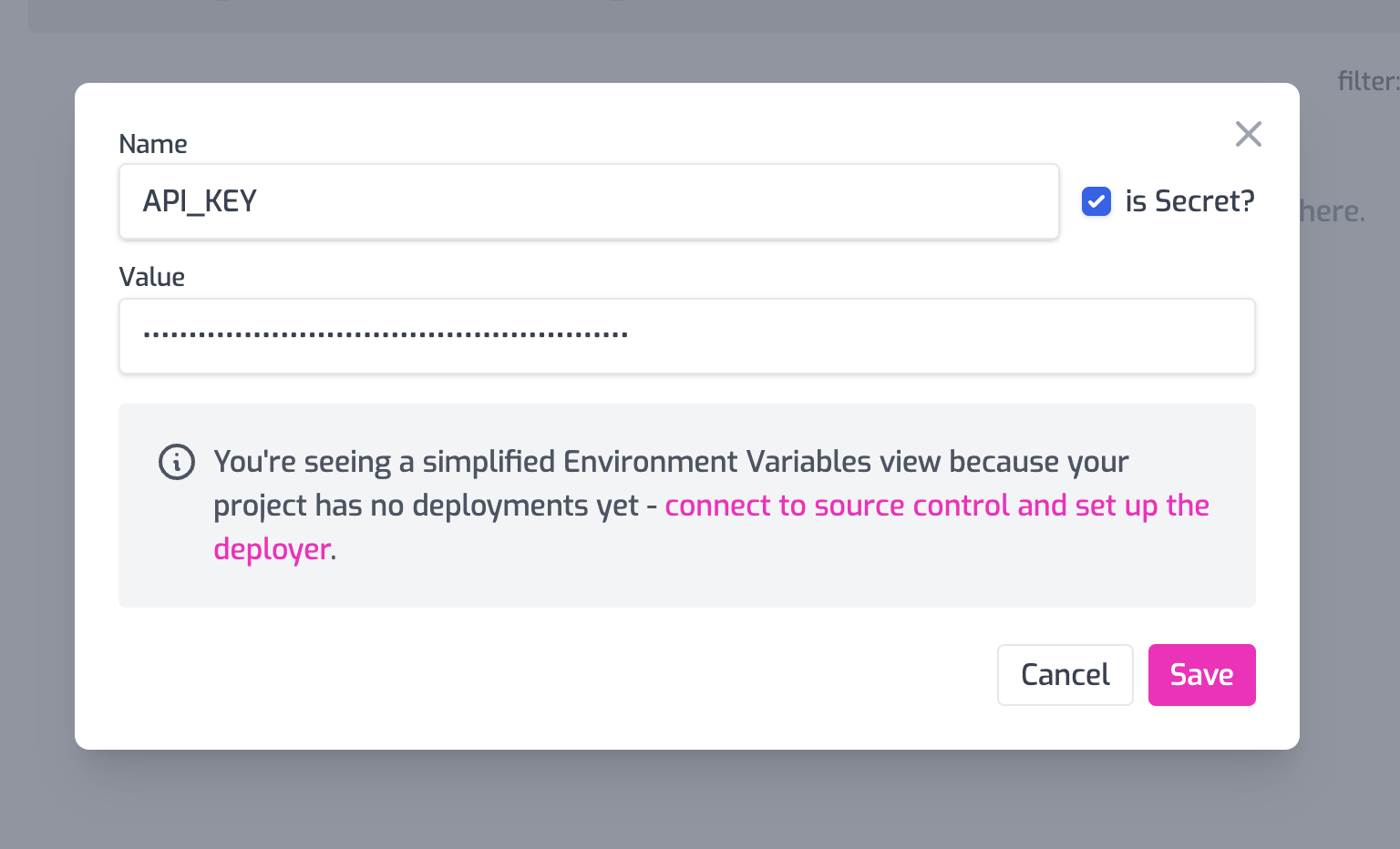
Set the name to API_KEY and select is Secret (the demo API key is not
really secret but if you use an API key to access your backend, that is an
important secret).
3/ Test your API#
Go back to your route in the Route Designer and click the Test button next to the Path field. Open the URL in the browser and you should see a list of todoitems.
[
{
"userId": 1,
"id": 1,
"title": "delectus aut autem",
"completed": false
},
{
"userId": 1,
"id": 2,
"title": "quis ut nam facilis et officia qui",
"completed": false
},
{
"userId": 1,
"id": 3,
Congratulations, your gateway is working 👏👏👏
4/ BONUS - put the base URL in an environment variable#
When working with Zuplo, you'll eventually want each environment to use a different backend (e.g. QA, staging, preview, production etc).
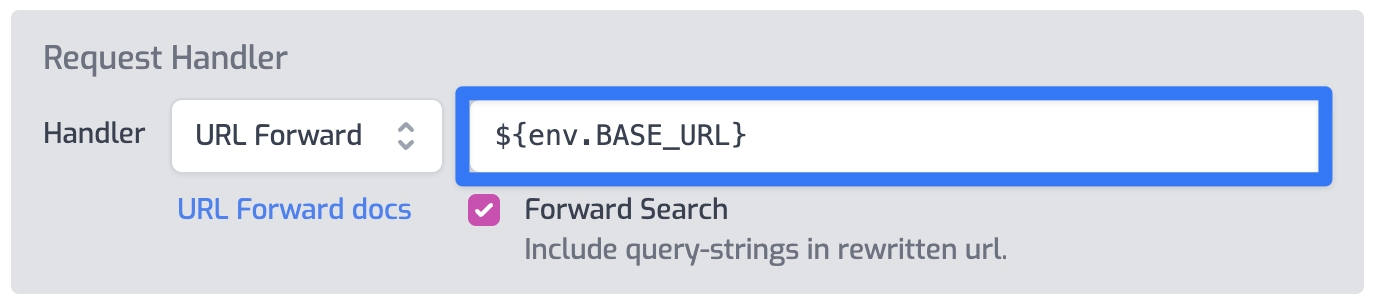
Change the URL Forward value to read the base URL from the
Environment Variables system by setting
the value to ${env.BASE_URL}.
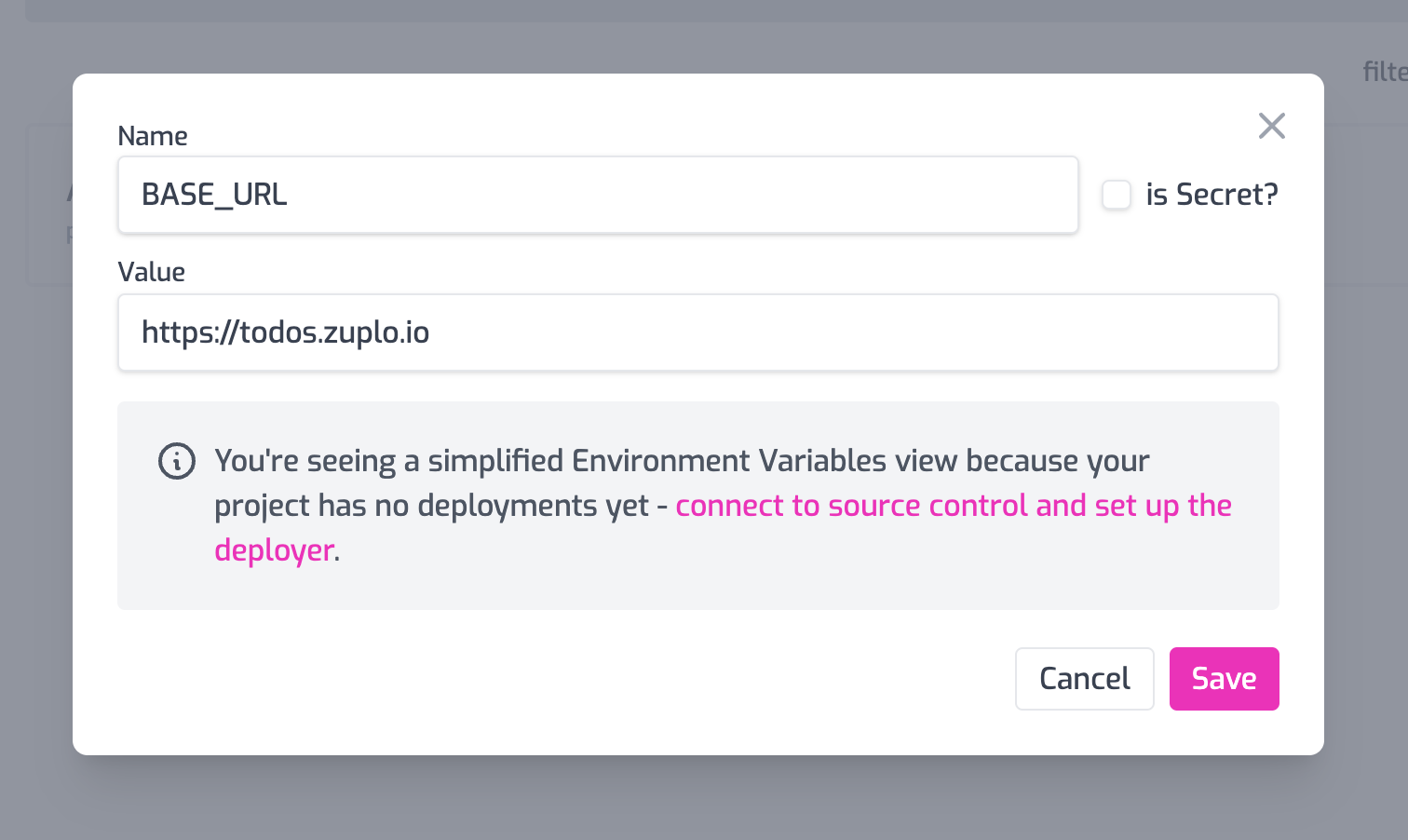
Add another Environment Variable called BASE_URL. This is typically not a secret, there's no need to hide this from your colleagues.
Save all your changes and test your route again.